Radiator
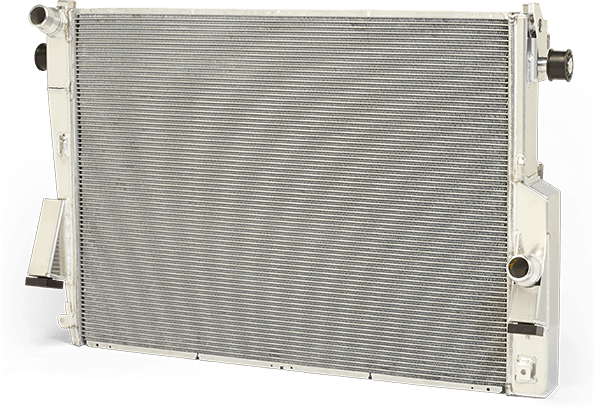
The main component of the cooling system, a radiator’s main purpose is to keep an engine at the optimal operating temperature, which it achieves by absorbing excess heat generated by the engine and lowering the coolant temperature with the air passing through the vehicle’s front grille. Every vehicle, including electric vehicles, is equipped with a radiator.
- Only the highest grade materials used in production
- Extensive in-house laboratory and assembly-line testing capabilities
- Drop-in fit for easy installation
- Equipped with accessory packs to accommodate various original equipment models
- Meet or exceed OE specifications for fit, form and function
- Transit-tested with robust packaging to shield part from damage in shipping
- All transmission & engine oil coolers meet or exceed OE standards

« You guys are so awesome. The new CU1725 radiator is here! Just opened it up and the packaging is perfect! I can’t thank you enough. » - Chase C.
Part Components
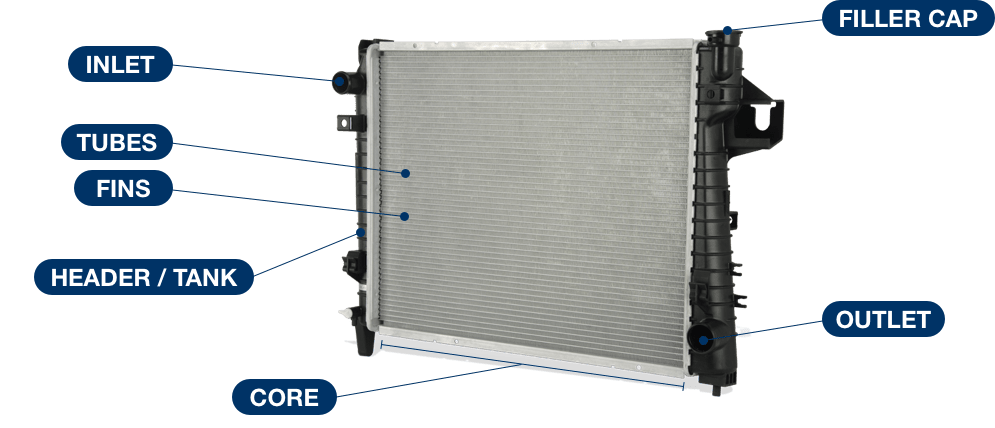
Other Spectra Premium radiators
- Auxiliary Radiator
- Radiator Core
- HD Radiator Core
- Radiator and AC Condenser Assembly
- Industrial engine radiator
Accessories available
- Radiator Mount
- Core gasket
- Coolant tester
- Radiator cap
Common Radiator Failure Symptoms
- Leaking coolant
- Overheating engine
- Deposits in the coolant
- Reducing coolant level
Common Causes of Failure
Electrolysis
Electrolysis problems appear when an electric current circulates in a cooling system. Electrolysis is the first cause of failure for aluminum radiators and has increased with the rising number of electric and electronic accessories.
Contamination
Cooling systems use a 1:1 mix of distilled water and antifreeze to absorb engine heat and protect against corrosion. Contaminated coolant increase the fluid acidity which wears down the aluminum until leaks start to appear.
Collision
As a front-end part, radiators are often involved in collisions. Even if the initial impact does not damage the radiator, smaller leaks in the cooling system can be found afterwards which also warrants radiator replacement.
Radiator replacement importance
When replacing your radiator, it is important to understand the root cause of failure: proper cooling system maintenance. It’s important to inspect the radiator pressure cap and thermostat for proper operation. The coolant reservoir needs to be inspected for cracks and leaks. The radiator cooling fan needs to be inspected for proper engagement. The water pump needs to be inspected for coolant leaks, and last but not least, the engine coolant needs to be tested for contamination. Performing a complete cooling system flush is strongly recommended when replacing any cooling system part.
Keep in mind that an engine that runs too cold is as bad as an engine that overheats. An overheating engine can produce temperatures around the combustion chamber (cylinder head) high enough to destroy cylinder heads and gaskets. A cold running engine, caused by a defective thermostat that is stuck open, will prevent the removal of condensation forming in the engine that can oxidize and create sludge build-up in the oil pan.